Overview and Specifications of WheelTop's Affordable Electronic Groupset "EDS"
This article summarizes the features and specifications of the budget-friendly electronic groupset "EDS" newly released by the Chinese manufacturer WheelTop.
Modified at: Oct 18, 2023
Posted at: Nov 29, 2021
Disc brakes are coming of age, and conventional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes. This article summarizes the differences between them and which is better.
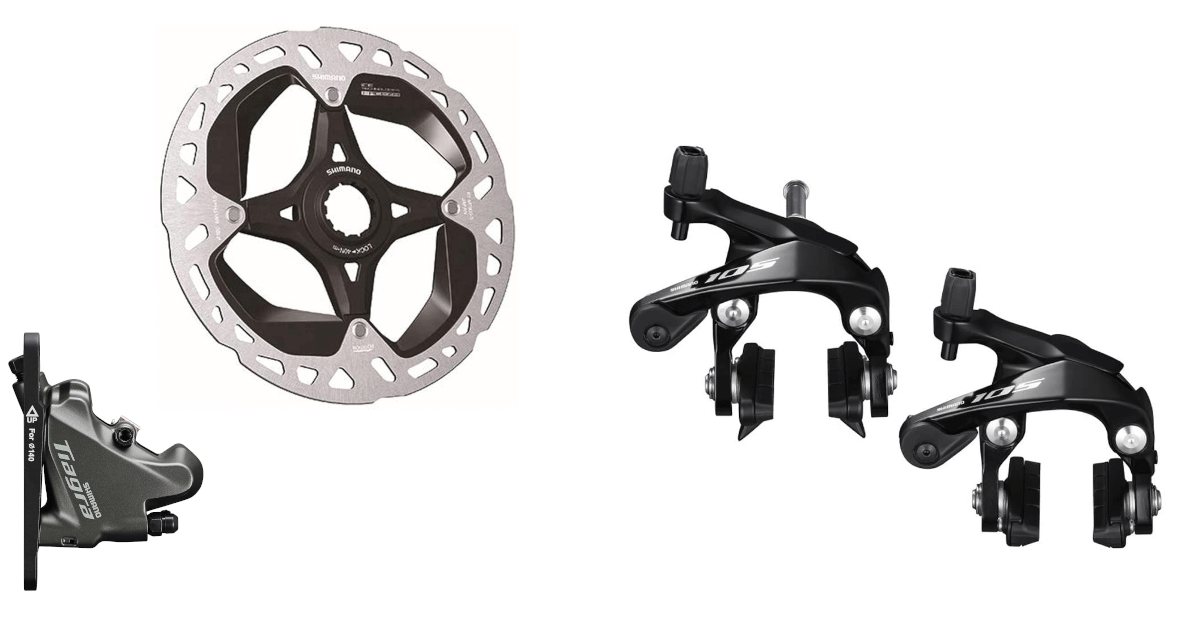
Table of contents
Sponsored Link
| Comparison Item | Disc Brakes | Rim Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Stopping Power | Similar for the same grade | Similar for the same grade |
| Braking Power in Wet Conditions | High | Low |
| Brake System Weight | Slightly heavier | Lighter |
| Wheel Lifespan | Longer due to less strain on the rim | Shorter depending on rim wear |
| Brake Pad Lifespan | Relatively long | Relatively short |
| Number of Parts Needing Adjustment | More | Fewer |
| Ease of Maintenance | Complex | Simple |
While disc brakes and rim brakes may seem very different, they actually operate on the same principle of “clamping to brake.”
Traditional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes clamp the rim of the wheel to brake, whereas disc brakes clamp a rotor attached to the wheel hub. However, both systems work by “clamping to brake,” making the fundamental mechanism the same.
Thus, the key difference is the location of the clamping, which, while subtle, results in significant differences in performance.
It is often said that “disc brakes have more stopping power than rim brakes,” but a more accurate statement is: “With hydraulic disc brakes, finer and stronger braking can be achieved compared to rim brakes.”
In terms of stopping power, V-brakes are quite powerful, and caliper brakes at higher grades also offer sufficient stopping power.
The difference comes in the initial application of the brakes. Hydraulic disc brakes start braking effectively from the moment the lever is pulled, while V-brakes and caliper brakes typically start braking effectively when the lever is pulled about 60-80% of the way.
This difference is the basis for the perception that “disc brakes work better.” While disc brakes certainly have their advantages, much of this comes down to the hydraulic aspect.
By the way, mechanical disc brakes, which are less precise in adjustment, are sometimes said to offer lower braking power than higher-grade rim brakes. However, high-performance mechanical disc brakes, like those in GROWTAC’s EQUAL series, have been developed to offer braking power comparable to hydraulic disc brakes.
Summary of mechanical disc brake calipers for road use
Mechanical disc brake calipers are easy to maintain and a low-cost way to upgrade from rim brake components to disc brakes. We have lined up models from major manufacturers and compared them.
The strength of disc brakes lies in their resistance to water, sand, and other contaminants.
In wet conditions, such as rain, rim brakes can experience a decrease in braking power. Water or sand can stick to the rim, reducing the coefficient of friction between the brake pads and the rim, leading to a drop in braking performance. This is because the rim is close to the road surface, and this cannot be avoided. In particular, for carbon rims, without using high-end carbon-specific brake pads, some cyclists feel that “the brakes barely work on rainy days.”
On the other hand, disc brakes are less affected by weather conditions because the disc rotor, which is clamped, is attached to the wheel hub, meaning the braking surface is distanced from the road. As a result, disc brakes are less influenced by road conditions, leading to less reduction in braking power in wet or muddy conditions.
Since road bikes are all-weather vehicles, cyclists sometimes ride in the rain. Especially for professionals, it’s not an option to skip races just because it’s raining, so choosing disc brakes that maintain braking power in wet conditions is a given.
Sponsored Link
Now, let’s compare the pros and cons of each brake type.
| Disc Brakes | Rim Brakes | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | ・Powerful braking for quick deceleration ・High braking performance in wet conditions ・Less strain on rims, leading to higher wheel durability |
・Lightweight brake system, reducing overall bike weight ・Easy maintenance, user-friendly for beginners ・Lower bike cost and repair expenses |
| Cons | ・Expensive brake system, raising bike price ・Heavier bike weight ・More complex maintenance |
・Lower braking power in wet conditions ・Shorter brake pad lifespan, requiring frequent replacements ・Rim wear progresses more quickly |
From this comparison, it becomes clear that disc brakes are not always the perfect solution.
In fact, some professional road cyclists prefer rim brakes, and the UCI WorldTour team Ineos Grenadiers, while many competing teams switched to disc brakes, continued to use rim brake bikes in actual races until mid-2021, citing that “the weight of disc brake bikes did not meet the team’s required level (they were too heavy).”
In the past, road bikes were commonly known for their “narrow rims and light weight,” but today, the trend is shifting towards “aero wheels” with high rim heights and superior aerodynamics, especially in road bikes.
Historically, in bicycle wheels, it was common knowledge that “deep-rim aero wheels = heavy” with metal rims. Due to weight concerns, aero wheels with high rim heights were typically avoided except in time trials. However, with advances in carbon fiber technology, it is now possible to make even deep-rim wheels lightweight by using carbon materials.
The focus on aerodynamics in cycling now extends beyond just frames and wheels to handlebars and helmets, becoming one of the key factors when choosing a bike.
The rims, which are essential parts of a bicycle wheel, are typically made of three main materials:
In recent years, the trend in high-performance bikes, especially road bikes, has been towards weight reduction, making it necessary to lighten components like the wheel rims, which contribute significantly to the bike’s overall weight.
In this context, carbon materials have become increasingly popular, particularly for higher-end wheels. While carbon is lighter than metal, it is more heat-sensitive. In rim brakes, which apply pressure to the rim to create friction, the heat generated by braking can deform or damage the rim.
This is where disc brakes have gained attention. Since disc brakes use a metal rotor for braking, the material of the rim has no impact on braking performance. This allows for both “lightweight carbon rims” and “prevention of rim deformation” to be achieved, leading to the industry’s shift toward disc brakes.
As a result, we are now in the era of hydraulic disc road bikes, with all high-end models from major road bike manufacturers now equipped with hydraulic disc brakes.
So, is it true that “rim brakes are over”? Not quite. There are still plenty of rim brake models available in entry-level to mid-range road bikes priced under 200,000 yen. For the next few years, rim brake models will likely coexist with disc brake models.
In fact, even after the “wave of disc brakes” started to rise in 2022, some major manufacturers have continued to produce road bikes with rim brakes.
Also, considering the used market, users who have switched to disc brakes may start releasing their rim brake assets (wheels, components, etc.), so the next few years may see an abundance of used rim brake options in the market.
Given this, rim brakes will likely remain the main option for the next 5 years. Eventually, the prices of disc brake complete bikes and parts will stabilize, so switching to them later won’t be an issue.
However, new rim brake models will likely become rarer in the future, leading to a decrease in the stock of new bikes. If you’re planning to use a rim brake bike for a while, it might be a good idea to purchase high-quality rim brake components and wheels within the next 1-2 years.
It’s important to understand that upgrading from rim brakes to disc brakes is generally not feasible.
To install disc brakes on a bike, the following four requirements must be met:
The biggest issue is with the rear end, as rim brake bikes typically have 130mm or 135mm quick-release dropouts, while most disc brake wheels use 142mm thru-axles (though some older bikes or 135mm quick-release disc frames exist). This means it is physically impossible to mount disc wheels on a rim brake bike.
This is one of the drawbacks of buying a rim brake bike at this point, so when purchasing, you may want to consider how long you’ll continue using that bike.
Road Bike to Disc Brakes Conversion: Parts Needed and Buying Tips
Disc brake-equipped road bikes have been on the rise in the past few years. "For those who want to try out disc brakes but don't want to buy a new bike, we've put together a list of the parts you'll need to buy disc brakes and the points to keep in mind when buying.
Types of Disc Brakes for Road Bikes
This page summarizes the types of disc brakes that can be installed on road bikes. Differences in mechanisms, rotors, and wheels/frames to install.
Sponsored Link
Road Bike to Disc Brakes Conversion: Parts Needed and Buying Tips
Disc brake-equipped road bikes have been on the rise in the past few years. "For those who want to try out disc brakes but don't want to buy a new bike, we've put together a list of the parts you'll need to buy disc brakes and the points to keep in mind when buying.
Differences and Identification of Disc Brake Only Wheels
Disc brake bicycles require wheels specially designed for disc brakes. In this article, we will discuss what is the difference between disc brake-specific wheels and rim brake-specific wheels. What is the difference between a disc brake wheel and a rim brake wheel? Or rim brake only? When selecting a wheel, it is important to know how to tell the difference.
Types of Disc Brakes for Road Bikes
This page summarizes the types of disc brakes that can be installed on road bikes. Differences in mechanisms, rotors, and wheels/frames to install.
Should I use disc brakes or rim brakes?
Disc brakes are coming of age, and conventional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes. This article summarizes the differences between them and which is better.
Shimano road disc brake component compatibility summary
Shimano disc brake components for road use are difficult to select if you don't know about them. We have compiled a list of parts model numbers and their incompatibility, which can be difficult to understand.
Types of disc brake rotors and how to select them
Disc brake rotors are an unassuming part, but they have a significant impact on the effectiveness of disc brakes. We have compiled a list of the different types of rotors, how to select one, and the lineup of rotors from major manufacturers.
What is a Through Axle? Types and How to Choose
Through-axle is becoming a major fixation method for disc brake wheels. What is a through-axle? Here is a summary of what types are available.
Disc brake pad types and selection
Brake pads are installed on the calipers of disc brakes. In fact, there are multiple types in terms of material and shape. The following is a summary of disc brake pad types and how to select the right one.
Bicycle Disc Brake Mounts: Recognition and Adapter Selection
Mounting adapters for bicycle disc brakes are essential when changing calipers with different standards or rotor sizes. This section explains the types of mount adapters, how to recognize them, and the model numbers of Shimano's mount adapters.
Center Lock Locking Rings: Inside and Outside Serrations
There are two types of lock rings for center locking disc brakes, inner serration and outer serration. The following is a summary of the differences and how to select the right one.
Summary of mechanical disc brake calipers for road use
Mechanical disc brake calipers are easy to maintain and a low-cost way to upgrade from rim brake components to disc brakes. We have lined up models from major manufacturers and compared them.
Types and Differences of Brakes for Sports Bicycles
Sports bicycles are equipped with various types of brakes. Here is a summary of each brake, its features and differences, advantages and disadvantages, and which brake bike you should buy in the future.
How to lighten heavy mechanical brakes.
The weight of the brakes not only affects the braking power, but also creates a significant impact on fatigue during the ride. In this article, we'll take a look at how mechanical brakes work and how you can lighten the weight of heavy brakes.
Selecting Shimano Brakes for Road Bikes: A Summary of Model Numbers
Brakes are an important part of a road bike that is responsible for braking. In this article, we will discuss how to select Shimano brakes for road bikes, which are of high quality and highly available in Japan, and summarize the model numbers of each grade of brake.
The higher the grade, the better it works! Brake shoe types and interchangeability
Of all the bicycle parts, brake shoes are the most frequently replaced along with tires and tubes. The following is a summary of the types of brake shoes and notes on compatibility, which are said to work better if they are used at the top level.
Shimano's older high-grade brakes vs. current lower-grade brakes: Which is better?
Which is better, Shimano's older generation higher grade brakes or the current lower grade brakes? This article examines Shimano's brake technology and the year they were released.
Road Bike to Disc Brakes Conversion: Parts Needed and Buying Tips
Disc brake-equipped road bikes have been on the rise in the past few years. "For those who want to try out disc brakes but don't want to buy a new bike, we've put together a list of the parts you'll need to buy disc brakes and the points to keep in mind when buying.
Differences and Identification of Disc Brake Only Wheels
Disc brake bicycles require wheels specially designed for disc brakes. In this article, we will discuss what is the difference between disc brake-specific wheels and rim brake-specific wheels. What is the difference between a disc brake wheel and a rim brake wheel? Or rim brake only? When selecting a wheel, it is important to know how to tell the difference.
Should I use disc brakes or rim brakes?
Disc brakes are coming of age, and conventional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes. This article summarizes the differences between them and which is better.
Overview and Specifications of WheelTop's Affordable Electronic Groupset "EDS"
This article summarizes the features and specifications of the budget-friendly electronic groupset "EDS" newly released by the Chinese manufacturer WheelTop.
What Is Shimano Shadow RD? Features and Benefits
What is Shimano’s Shadow RD used in their latest rear derailleurs? This article explains its features and the benefits of choosing Shadow RD.
[MTB / Hybrid Bike] Hydraulic Brake Manufacturers for Flat Bars
An overview of manufacturers that produce hydraulic brakes for flat-bar MTB and hybrid bikes, along with their key features. Also includes tips on how to choose the right flat-bar hydraulic brake brand.
Shimano Chain Compatibility for Road, MTB, and Hybrid Bikes
An overview of Shimano chain compatibility across road bikes, mountain bikes, and hybrid bikes. Includes guidance on how to choose the right chain for your drivetrain.
Shimano ESSA Lineup and Compatibility with Existing 8-Speed Parts
An overview of Shimano's newly released 8-speed component group "ESSA" and its compatibility with existing 8-speed parts.
SRAM Cassette Compatibility Guide
Compatibility guide for SRAM cassettes used in road and MTB bikes. Find matching drivetrains and wheels easily.
Compatibility Guide for SRAM MTB Components
A detailed explanation of compatibility between SRAM MTB components. This guide outlines which parts can be used together and which combinations are not compatible.
Road and MTB Sprockets Compatibility Overview
A guide to the compatibility between road and MTB sprockets, explaining whether they can be used together with different components.
Types of Shimano Di2 Tools and Their Compatibility
A guide to the essential Shimano Di2-specific tools, especially the "plug tools" used for connecting components, and their compatibility with various Di2 parts.
Shimano CUES Cassette Compatibility Guide
A detailed guide to the compatibility of Shimano CUES series cassettes. Includes an overview of compatible rear derailleurs, chains, and wheels.
Shimano Hydraulic Brake Hose and Connector Standards Guide
An explanation of the differences between Shimano’s hydraulic brake hoses BH90 and BH59, the types of connecting bolts, and how to choose the right hose for your brake system—including key points to watch out for.
[By Manufacturer] Types, Features, Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Brake Oils
This article explains the types of hydraulic oils used in bicycle hydraulic brakes, their characteristics, and the brake oil types used by each manufacturer.
Types and Compatibility of Shimano Di2 Batteries
The Di2 battery is the core of the Shimano Di2 system, influencing the overall system layout. This article explains the different types and their compatibility.
Shimano Di2 Wire Types and Compatibility
Overview of Shimano Di2 electric wire types and their compatibility with Di2 components.
How to Identify Shimano Di2 Generations
Explains the generational differences in Shimano Di2 components and their compatibility. Includes a list of component series and their corresponding generations.
In-Depth Guide to Shimano 12-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of the key compatibility factors when using Shimano's 12-speed cassettes—specifically the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain, which differ significantly from previous 11-speed systems.
Perfect Guide to Shimano 11-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 11-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
Perfect Guide to Shimano 10-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 10-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
In-Depth Guide to Shimano 9-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A comprehensive explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 9-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
What Is a BOOST Crank? Differences from Standard MTB Cranks and How to Choose
This article explains what a BOOST crank is, how it differs from conventional MTB cranks, and provides guidance on selection across different manufacturers.