Overview and Specifications of WheelTop's Affordable Electronic Groupset "EDS"
This article summarizes the features and specifications of the budget-friendly electronic groupset "EDS" newly released by the Chinese manufacturer WheelTop.
Posted at: Dec 27, 2023
Rotor size is a key factor affecting the performance of bicycle disc brakes. This article explains how rotor size impacts braking, the features of common sizes, their advantages, ideal use cases, and how to choose the right size for your riding style.
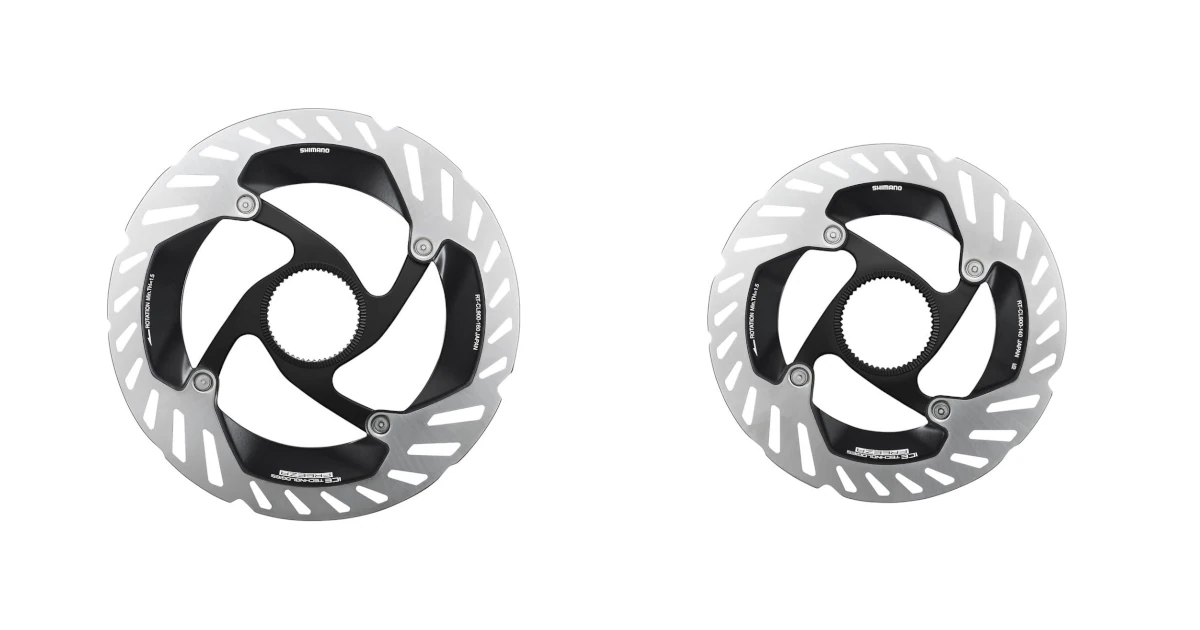
Table of contents
Sponsored Link
Bicycle disc rotors come in sizes such as 140mm, 160mm, 180mm, and 203mm. When the size changes, the following aspects are mainly affected.
The braking power of disc brakes is “proportional to the torque (force applied to the rotor) and the radius of the disc rotor.” It’s similar to how it’s easier to turn a larger handle than a smaller one.
In the same way, if the braking force is constant, a larger disc rotor will provide greater braking power.
In a disc brake system, the bike’s kinetic energy is converted into thermal energy by squeezing the rotor to slow the bike down. If the rotor is too hot, braking performance can decrease.
The converted thermal energy is released into the air through the rotor. As the rotor size increases, the surface area increases, improving heat dissipation.
However, the heat dissipation performance of a rotor is not only dependent on its size but also on the manufacturer’s unique heat dissipation technology (such as Shimano’s ICE technology), so smaller rotors do not necessarily mean poorer heat dissipation.
As seen above, rotor size affects both braking power and heat dissipation, which in turn impacts braking performance.
For example, a smaller rotor provides less braking power, which allows for more precise braking, while a larger rotor has more braking power, making the braking more forceful.
Since disc rotors are made of metal plates, the larger the size, the greater the physical surface area, and thus the heavier the rotor becomes. Changing the rotor size can result in a weight difference of up to 100g.
Although the weight of the rotor only accounts for a few percent of the total bike weight, for users looking to make their bike as light as possible, a 100g difference can be significant.
| Size | Advantages | Disadvantages | Optimal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 140mm | Lightweight Allows for agile handling |
Braking power is lower compared to other sizes Not suitable for long downhill rides |
General use with a lightweight, non-aggressive setup |
| 160mm | Good balance of lightness and braking power | Braking power may be a bit low for MTB front brakes | Urban commuting and light off-road riding |
| 180mm | Moderate braking power and heat dissipation Ideal for general mountain biking and trail riding |
Heavier than 160mm and might be excessive for some riders Can significantly impact handling |
Mountain biking and trail riding |
| 203mm | High braking power and effective heat dissipation | Heavy, unsuitable for lightweight bikes | Downhill, enduro, and aggressive trail riding |
The 140mm rotor is mainly used on the rear brakes of disc road bikes. With its smaller size, it is lightweight and can still provide sufficient braking power when paired with hydraulic brakes.
While it offers less braking power than a 160mm rotor, rear brakes are typically used for speed control. In road biking, if there aren’t any long, steep descents, a 140mm rotor provides enough braking power.
The 160mm size is commonly selected as the standard rotor size for road bikes, gravel bikes, and cross-country MTB. It is the most popular size for modern sport bicycles. For flat mount road bike brakes, 160mm is the maximum size.
Compared to the 140mm, it provides more braking power, and its weight is kept around 100g for higher-end models, making it the most balanced disc rotor size.
The 180mm size is a popular choice for MTB front brakes. In addition to higher braking power, a larger rotor offers better heat dissipation.
When braking for extended periods, heat buildup can reduce braking performance. However, with a 180mm rotor, the increased surface area of the rotor helps to dissipate heat effectively.
The 203mm size is used for MTB downhill and enduro riding. This size is ideal for downhill and enduro MTB where high braking power is needed quickly, especially when riding steep hills or encountering obstacles.
The large rotor size does add weight, which is a disadvantage.
The most important factor is selecting a rotor size that suits your riding style.
For example, if you’re using a bike for city commuting, you likely won’t reach high speeds, so a 140mm rotor will be sufficient. However, if you’re cruising at 40km/h on a road bike or enjoying downhill hill climbs, a 160mm rotor will provide more reliable braking.
However, higher braking power doesn’t always mean better performance. As explained earlier, while higher braking power increases braking force, it can also make fine adjustments to braking more difficult, and if you’re not accustomed to it, you may end up with sudden, hard stops.
Sudden braking can increase the risk of falls or endos, so it’s important to choose a rotor size that allows you to brake appropriately, rather than simply focusing on maximum braking power.
Whether it’s a road bike or an MTB, “lightness is key” is often said, and weight is a crucial factor.
The larger the rotor size, the heavier it becomes. While you may want to reduce weight by using a smaller rotor, prioritizing lightness to the point where braking power is compromised could lead to accidents.
Therefore, it’s important to strike a balance between achieving a lighter setup while ensuring that you have enough braking power to control the bike effectively.
Sponsored Link
Road Bike to Disc Brakes Conversion: Parts Needed and Buying Tips
Disc brake-equipped road bikes have been on the rise in the past few years. "For those who want to try out disc brakes but don't want to buy a new bike, we've put together a list of the parts you'll need to buy disc brakes and the points to keep in mind when buying.
Differences and Identification of Disc Brake Only Wheels
Disc brake bicycles require wheels specially designed for disc brakes. In this article, we will discuss what is the difference between disc brake-specific wheels and rim brake-specific wheels. What is the difference between a disc brake wheel and a rim brake wheel? Or rim brake only? When selecting a wheel, it is important to know how to tell the difference.
Types of Disc Brakes for Road Bikes
This page summarizes the types of disc brakes that can be installed on road bikes. Differences in mechanisms, rotors, and wheels/frames to install.
Should I use disc brakes or rim brakes?
Disc brakes are coming of age, and conventional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes. This article summarizes the differences between them and which is better.
Shimano road disc brake component compatibility summary
Shimano disc brake components for road use are difficult to select if you don't know about them. We have compiled a list of parts model numbers and their incompatibility, which can be difficult to understand.
Types of disc brake rotors and how to select them
Disc brake rotors are an unassuming part, but they have a significant impact on the effectiveness of disc brakes. We have compiled a list of the different types of rotors, how to select one, and the lineup of rotors from major manufacturers.
What is a Through Axle? Types and How to Choose
Through-axle is becoming a major fixation method for disc brake wheels. What is a through-axle? Here is a summary of what types are available.
Disc brake pad types and selection
Brake pads are installed on the calipers of disc brakes. In fact, there are multiple types in terms of material and shape. The following is a summary of disc brake pad types and how to select the right one.
Bicycle Disc Brake Mounts: Recognition and Adapter Selection
Mounting adapters for bicycle disc brakes are essential when changing calipers with different standards or rotor sizes. This section explains the types of mount adapters, how to recognize them, and the model numbers of Shimano's mount adapters.
Center Lock Locking Rings: Inside and Outside Serrations
There are two types of lock rings for center locking disc brakes, inner serration and outer serration. The following is a summary of the differences and how to select the right one.
Summary of mechanical disc brake calipers for road use
Mechanical disc brake calipers are easy to maintain and a low-cost way to upgrade from rim brake components to disc brakes. We have lined up models from major manufacturers and compared them.
Types and Differences of Brakes for Sports Bicycles
Sports bicycles are equipped with various types of brakes. Here is a summary of each brake, its features and differences, advantages and disadvantages, and which brake bike you should buy in the future.
How to lighten heavy mechanical brakes.
The weight of the brakes not only affects the braking power, but also creates a significant impact on fatigue during the ride. In this article, we'll take a look at how mechanical brakes work and how you can lighten the weight of heavy brakes.
Selecting Shimano Brakes for Road Bikes: A Summary of Model Numbers
Brakes are an important part of a road bike that is responsible for braking. In this article, we will discuss how to select Shimano brakes for road bikes, which are of high quality and highly available in Japan, and summarize the model numbers of each grade of brake.
The higher the grade, the better it works! Brake shoe types and interchangeability
Of all the bicycle parts, brake shoes are the most frequently replaced along with tires and tubes. The following is a summary of the types of brake shoes and notes on compatibility, which are said to work better if they are used at the top level.
Shimano's older high-grade brakes vs. current lower-grade brakes: Which is better?
Which is better, Shimano's older generation higher grade brakes or the current lower grade brakes? This article examines Shimano's brake technology and the year they were released.
Road Bike to Disc Brakes Conversion: Parts Needed and Buying Tips
Disc brake-equipped road bikes have been on the rise in the past few years. "For those who want to try out disc brakes but don't want to buy a new bike, we've put together a list of the parts you'll need to buy disc brakes and the points to keep in mind when buying.
Differences and Identification of Disc Brake Only Wheels
Disc brake bicycles require wheels specially designed for disc brakes. In this article, we will discuss what is the difference between disc brake-specific wheels and rim brake-specific wheels. What is the difference between a disc brake wheel and a rim brake wheel? Or rim brake only? When selecting a wheel, it is important to know how to tell the difference.
Should I use disc brakes or rim brakes?
Disc brakes are coming of age, and conventional rim brakes such as caliper brakes and V-brakes. This article summarizes the differences between them and which is better.
Overview and Specifications of WheelTop's Affordable Electronic Groupset "EDS"
This article summarizes the features and specifications of the budget-friendly electronic groupset "EDS" newly released by the Chinese manufacturer WheelTop.
What Is Shimano Shadow RD? Features and Benefits
What is Shimano’s Shadow RD used in their latest rear derailleurs? This article explains its features and the benefits of choosing Shadow RD.
[MTB / Hybrid Bike] Hydraulic Brake Manufacturers for Flat Bars
An overview of manufacturers that produce hydraulic brakes for flat-bar MTB and hybrid bikes, along with their key features. Also includes tips on how to choose the right flat-bar hydraulic brake brand.
Shimano Chain Compatibility for Road, MTB, and Hybrid Bikes
An overview of Shimano chain compatibility across road bikes, mountain bikes, and hybrid bikes. Includes guidance on how to choose the right chain for your drivetrain.
Shimano ESSA Lineup and Compatibility with Existing 8-Speed Parts
An overview of Shimano's newly released 8-speed component group "ESSA" and its compatibility with existing 8-speed parts.
SRAM Cassette Compatibility Guide
Compatibility guide for SRAM cassettes used in road and MTB bikes. Find matching drivetrains and wheels easily.
Compatibility Guide for SRAM MTB Components
A detailed explanation of compatibility between SRAM MTB components. This guide outlines which parts can be used together and which combinations are not compatible.
Road and MTB Sprockets Compatibility Overview
A guide to the compatibility between road and MTB sprockets, explaining whether they can be used together with different components.
Types of Shimano Di2 Tools and Their Compatibility
A guide to the essential Shimano Di2-specific tools, especially the "plug tools" used for connecting components, and their compatibility with various Di2 parts.
Shimano CUES Cassette Compatibility Guide
A detailed guide to the compatibility of Shimano CUES series cassettes. Includes an overview of compatible rear derailleurs, chains, and wheels.
Shimano Hydraulic Brake Hose and Connector Standards Guide
An explanation of the differences between Shimano’s hydraulic brake hoses BH90 and BH59, the types of connecting bolts, and how to choose the right hose for your brake system—including key points to watch out for.
[By Manufacturer] Types, Features, Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Brake Oils
This article explains the types of hydraulic oils used in bicycle hydraulic brakes, their characteristics, and the brake oil types used by each manufacturer.
Types and Compatibility of Shimano Di2 Batteries
The Di2 battery is the core of the Shimano Di2 system, influencing the overall system layout. This article explains the different types and their compatibility.
Shimano Di2 Wire Types and Compatibility
Overview of Shimano Di2 electric wire types and their compatibility with Di2 components.
How to Identify Shimano Di2 Generations
Explains the generational differences in Shimano Di2 components and their compatibility. Includes a list of component series and their corresponding generations.
In-Depth Guide to Shimano 12-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of the key compatibility factors when using Shimano's 12-speed cassettes—specifically the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain, which differ significantly from previous 11-speed systems.
Perfect Guide to Shimano 11-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 11-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
Perfect Guide to Shimano 10-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A detailed explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 10-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
In-Depth Guide to Shimano 9-Speed Cassette Compatibility
A comprehensive explanation of two key compatibility factors when using Shimano 9-speed cassettes: the required wheel (freehub) and drivetrain.
What Is a BOOST Crank? Differences from Standard MTB Cranks and How to Choose
This article explains what a BOOST crank is, how it differs from conventional MTB cranks, and provides guidance on selection across different manufacturers.